Markov Decison Process (MDP)
1. Markov Decision Process
Markov Decision Process에서 상태의 전이가 일어날 경우, 미래의 상태 (State) 와 보상 (Reward) 는 오직 현재의 State 와 Reward 에 의해 결정됨
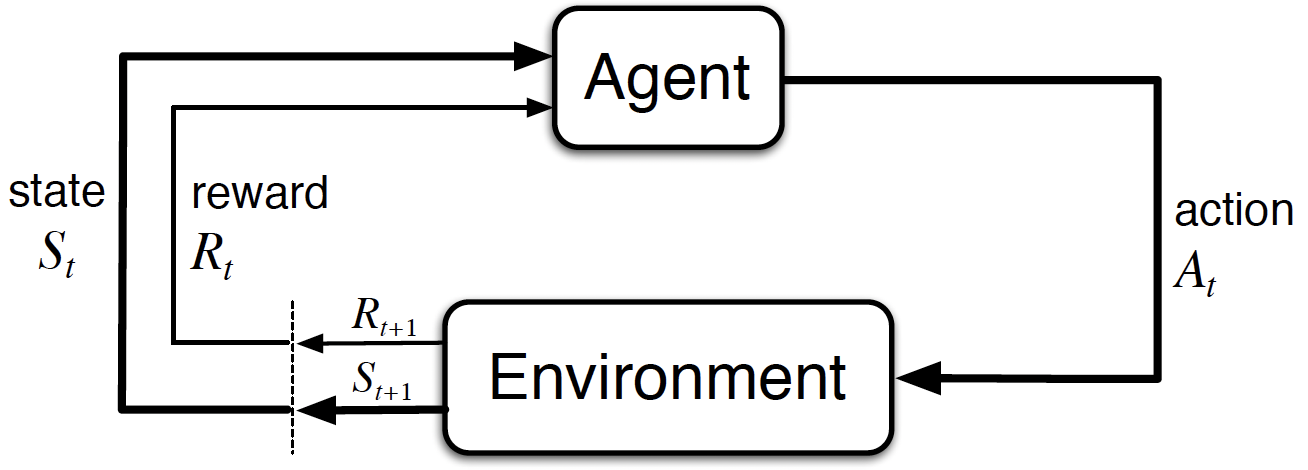
1-1. Agent-Environment Structure
Agent: RL에서 환경을 학습 (learn)하고, 행동 (Action)을 결정 (decision making)
Environment: Agent와 상호작용하는 외부의 환경
Set of state: \(s \in \mathcal{S}\)
Set of actions: \(A(s) \in \mathcal{A}\)
Set of rewards: \(r \in \mathcal{R} \subset \mathbb{R}\)
Trajectory (Finte MDP case): \(S_0, A_0, R_1, S_1, A_1, R_2, \cdots, S_{T-1}, A_{T-1}, R_{T}\)
Goal of Agent: 주어진 State 에서 누적된 보상 (Accumulated reward: \(\mathbb{E}[G_t]\) )을 최대화하는 행동을 결정
1-2. Dynamics of MDP
MDP의 Dynamics를 안다는 것은 Environment의 모든 State와 모든 Action에 대해, state transition probabilty를 아는 것과 동일한 의미 (일반적인 강화학습 문제에서는 MDP의 Dynamics를 알지 못함)
- State transition probability:
- Expected reward:
1-3. Policy and Value Functions
Policy: 어떤 State에서 행동 가능한 Action에 대한 확률
- Agent가 Policy \(\pi\)를 따르는 경우, \(\pi(a|s) \triangleq \mathcal{Prob}(A_t=a|S_t=s)\)
State-Value function: Policy \(\pi\)를 따르는 경우, State \(s\) 에서의 누적 보상에 대한 기대값 (Agent가 특정 상태에 있는 것이 얼마나 좋은지 판단)
\[v_{\pi}(s) \triangleq \mathbb{E}_{\pi}\left[G_t|S_t=s\right]\]Action-Value function (Q-function): Policy \(\pi\)를 따르는 경우, State \(s\)에서 Action \(a\)를 수행하였을 경우 누적 보상에 대한 기대값 (Agent가 특정 상태에서 어떤 행동을 수행하는 것이 얼마나 좋은지 판단)
\[q_{\pi}(s, a) \triangleq \mathbb{E}_{\pi}\left[G_t|S_t=s, A_t=a \right]\]
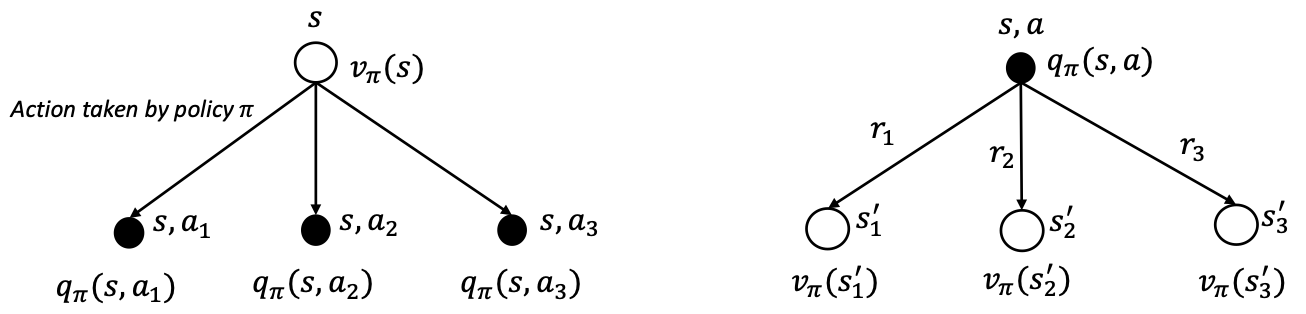
1-4. Relationship between State-Value Function and Action-Value Function
Value function의 정의와 backup diagram을 참고하면 다음과 같은 관계식을 도출할 수 있다.
\[(1) \ v_{\pi}(s) = \mathbb{E}_{\pi}\left[G_t|S_t=s\right] = \sum_{a} \pi(a|s) \mathbb{E}_{\pi}\left[G_t|S_t=s, A_t=a \right] = \sum_{a} \pi(a|s)q_{\pi}(s, a)\] \[(2) \ q_{\pi}(s, a) = \mathbb{E}_{\pi}\left[G_t|S_t=s, A_t=a \right] = \sum_{s'}\sum_{r}p(s', r|s, a)\left\{ r + \gamma \mathbb{E}_{\pi} \left[ G_{t+1}| S_{t+1}=s' \right] \right\} = \sum_{s'}\sum_{r}p(s', r|s, a) \left\{ r + \gamma v_{\pi}(s') \right\}\]