DQN example - Cartpole
1. Introduction
본 포스팅에서는 OpenAI Gym의 Cartpole 환경을 예시로 들어서 앞선 포스팅에서 다룬 DQN 알고리즘을 구현하는 코드에 대해 다룬다. 본 포스팅에서 다룬 코드를 실행시키기 위해 필요한 Python Package는 (gym > 0.21 또는 gymnasium), numpy, matplotlib, pytorch 이다.
2. Cartpole
Cartpole 환경에서 agent의 목적은 매 time-step 마다 폴대가 쓰러지지 않도록 폴을 왼쪽 또는 오른쪽으로 움직이도록 행동하는 것이다. 앞선 포스팅에서 다루었듯이 Continuous State 환경으로 구성되어 있고, 2개의 discrete한 action으로 구성되어 있다. 특히 gym v0.22 부터 제공되는 환경은 이전 버전에서 제공되던 환경과 큰 변화가 생겼으므로 관련된 변화도 같이 설명한다.
2-1. State
- 카트의 위치 (Cart position): $-4 \sim 4$
- 카트의 속도 (Cart velocity): $-\infty \sim \infty$
- 폴의 각도 (Pole angle[radian]): $-0.418 \sim 0.418$
- 폴의 각속도 (Pole angular velocity): $-\infty \sim \infty$
2-2. Action
- 0: 왼쪽으로 이동
- 1: 오른쪽으로 이동
2-3. Termination 조건
- 카트 폴 각도의 절대값이 12도를 초과하는 경우
- 카트 폴의 위치의 절대값이 2.4를 초과하는 경우 (edge에 도달)
- 버림(Truncation): time-step이 특정 횟수 이상을 초과하는 경우 (Cartpole-v0의 경우 200, Cartpole-v1의 경우 500)
gym v0.22부터 새롭게 버림 조건이 추가되었으며 버림 조건을 제외하고, termination이 발생한 경우 올바른 action이 수행되지 않아 폴대가 쓰러진 상황을 의미한다.
3. Implementation
3-1. Gymnasium Environment: Cartpole-v1
본 포스팅에서 다루는 DQN 예제에서는 gymnasium-0.28.1 에서 제공하는 Cartpole-v1 환경을 가정한다. 모델은 다음과 같이 생성할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
import gymnasium as gym
env = gym.make('Cartpole-v1')
Cartpole 환경 초기화를 위해서는 다음과 같이 코드를 작성한다.
1
2
3
state, info = env.reset()
gym v0.22 부터 info 라는 추가 정보가 반환되도록 변경되었으나, 본 포스팅에서는 info를 사용하지 않으므로 환경 초기화를 다음과 같이 처리하고, state를 $1 \times 4$의 2차원의 벡터로 변환시키기 위해 numpy의 expand_dims 함수를 아래와 같이 사용한다.
1
2
3
4
state, _ = env.reset()
state = np.expand_dims(state, axis=0)
다음으로 매 time-step 마다 agent에 의한 action을 입력 받아 다음 상태와 보상을 추출하기 위해 아래과 같이 step method를 호출한다.
1
2
3
next_state, reward, done, truncated, info = env.step(action)
위의 코드는 현재 상태에서 0 또는 1의 action을 수행했을 경우, 다음 상태 (next_state), 보상 (reward), 종료 여부 (done), 버림 조건 여부 (truncated), 추가 정보 (info)를 반환하는 것을 의미한다. gym v0.22 부터 버림 조건을 의미하는 truncated 변수가 추가로 리턴되는 것이 이전 버전과 비교하였을 때 유의미한 차이점이다. 환경 초기화 시와 마찬가지로 info는 본 포스팅에서 사용하지 않으므로 agent가 수행한 action에 대한 다음 상태 정보를 얻기 위해 아래와 같이 처리한다.
1
2
3
next_state, reward, done, truncated, _ = env.step(action)
3-2. DQN Model
1개의 input layer, 2개의 hidden layer, 1개의 output layer로 구성된 간단한 신경망 모델을 고려한다. 본 포스팅에서는 Pytorch를 사용하여 Class 기반으로 신경망을 설계하였고, 1번째 hidden layer를 구성하는 뉴런의 개수와 2번째 hidden layer를 구성하는 뉴런의 개수는 각각 32, 64로 설정한다. Hidden layer의 activation function은 ReLU를 사용하고, 학습 안정화를 위해 batch normalization을 적용한다. 신경망의 input layer와 output layer는 Class의 매개 변수로 입력된 값에 의해 뉴런의 개수가 결정되도록 구현되었고, Cartpole 환경에서 input layer의 뉴런의 개수는 state 구성 변수 개수(4)가 되고, output layer의 뉴런의 개수는 agent가 취하는 행동의 개수(2) 이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
import random
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class DQN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_input_layers, num_output_layers, batch_norm=True):
super().__init__()
self.num_input_layers = num_input_layers
self.num_output_layers = num_output_layers
self.batch_norm = batch_norm
self.setup_model()
self.apply(self._init_weights)
self._init_final_layer()
def _init_weights(self, module):
if isinstance(module, nn.Linear):
nn.init.kaiming_uniform_(module.weight.data, nonlinearity='relu')
if module.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(module.bias.data, 0)
elif isinstance(module, nn.BatchNorm1d):
nn.init.constant_(module.weight.data, 1)
nn.init.constant_(module.bias.data, 0)
def _init_final_layer(self):
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.layer3.weight.data)
def setup_model(self):
self.layer1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(self.num_input_layers, 32), nn.BatchNorm1d(32), nn.ReLU())
self.layer2 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(32, 64), nn.BatchNorm1d(64), nn.ReLU())
self.layer3 = nn.Linear(64, self.num_output_layers)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
return x
def greedy_action(self, state):
out = self.forward(state)
return out.argmax().item()
3-3. DQN Agent
설계한 DQN 모델을 기반으로 Agent를 학습시키기 위한 DQNAgent 클래스와 누적된 transition을 저장하기 위한 ReplayBuffer 클래스를 정의한다. DQN Agent에서는 main network의 학습 안정성을 위해 target network를 정의한다.
3-3-1. DQNAgent 클래스 구성 주요 method
soft_update(): target network가 main network의 weight를 일정 비율 (tau) 만큼 추적하여 업데이트한다.
train(): batch_size를 매게 변수로 받아서 replay buffer에서 임의로 batch_size 만큼의 transition을 추출하여 학습한다. 로컬 변수 q_a와 q_target은 각각 아래 수식에서 $L = R_{t+1} + \gamma \max_{a’}Q(S_{t+1}, a’ | \theta^{-})$ 와 $Q(S_t, A_t | \theta)$ 임을 확인한다. Transition에서 얻은 next state가 종료 상태의 state인 경우, Q-value 값을 구하지 않기 위해 done_mask를 활용한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
import torch
import random
from model_utils.dqn_model import DQN
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import collections
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
class DQNAgent():
def __init__(self, num_input_layers, num_output_layers, gamma=0.99, tau=0.1, learning_rate=1e-3, max_memory_size=50000,
batch_norm=True):
self.num_input_layers = num_input_layers
self.num_output_layers = num_output_layers
self.gamma = gamma
self.tau = tau
# Main network
self.dqn_net = DQN(num_input_layers=self.num_input_layers, num_output_layers=self.num_output_layers,
batch_norm=batch_norm).to(device)
# Target network
self.dqn_target = DQN(num_input_layers=self.num_input_layers, num_output_layers=self.num_output_layers,
batch_norm=batch_norm).to(device)
for target_param, param in zip(self.dqn_target.parameters(), self.dqn_net.parameters()):
target_param.data.copy_(param.data)
# Replay Buffer
self.memory = ReplayBuffer(num_input_layers, max_memory_size)
# Optimizer
self.criterion = nn.MSELoss()
self.optimizer = optim.Adam(self.dqn_net.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
def get_action(self, state):
state = torch.from_numpy(state).float()
self.dqn_net.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
out = self.dqn_net(state.to(device))
self.dqn_net.train()
return out.argmax().item()
def get_sample_action(self, state, epsilon):
coin = random.random()
if coin < epsilon:
return random.randint(0,1)
else:
return self.get_action(state)
def train(self, batch_size):
states, actions, rewards, next_states, done_mask = self.memory.sample(batch_size)
states = torch.FloatTensor(np.array(states))
actions = torch.tensor(actions).type(torch.int64)
rewards = torch.FloatTensor(np.array(rewards)).unsqueeze(1)
next_states = torch.FloatTensor(np.array(next_states))\
done_mask = torch.FloatTensor(done_mask)
q_out = self.dqn_net(states.to(device).view(batch_size, -1))
q_a = q_out.gather(dim=1, index=actions.to(device).view(-1, 1))
q_prime_target = self.dqn_target(next_states.to(device).view(batch_size, -1))
max_q_prime_target = q_prime_target.max(dim=1)[0].view(-1, 1)
q_target = rewards.to(device) + self.gamma * max_q_prime_target * (1 - done_mask).to(device).view(-1, 1)
loss = self.criterion(q_a, q_target)
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
self.optimizer.step()
def soft_update(self):
for target_param, net_param in zip(self.dqn_target.parameters(), self.dqn_net.parameters()):
target_param.data.copy_(self.tau * net_param.data + (1.0 - self.tau) * target_param.data)
class ReplayBuffer():
def __init__(self, num_input_layers, buffer_limit):
self.num_input_layers = num_input_layers
self.buffer = collections.deque(maxlen=buffer_limit)
def put(self, transition):
self.buffer.append(transition)
def sample(self, batch_size):
mini_batch = random.sample(self.buffer, batch_size)
state_batch = []
action_batch = []
reward_batch = []
next_state_batch = []
done_mask_batch = []
for transition in mini_batch:
state, action, reward, next_state, done_mask = transition
state_batch.append(state)
action_batch.append(action)
reward_batch.append(reward)
next_state_batch.append(next_state)
done_mask_batch.append(done_mask)
return state_batch, action_batch, reward_batch, next_state_batch, done_mask_batch
def size(self):
return len(self.buffer)
3-4. Main 함수
앞서 작성하였던 클래스를 통합하여 DQN 알고리즘 기반으로 Cartpole 환경에 대한 agent를 학습시킨다. target network는 episode 10회 마다 한번씩 soft update 되도록 구현하였고, 학습은 replay buffer의 크기가 500보다 큰 경우부터 이루어지도록 하였다. dqn() 함수에서 agent를 학습 시키기 위한 주요 hyper parameter는 다음과 같다.
- 학습 episode 개수: 500
- Discount rate $\gamma$: 0.99
- Replay memory 크기: 30000
- 학습 batch 크기: 64
- Start epsilon: 1.0
- Minimum epsilon: 0.01
- Epsilon decay rate: 0.99
- learning rate: 0.001
Gymnasium이 제공하는 Cartpole 함수의 default reward는 다음 step으로 넘어갈 때 마다 +1의 reward를 제공하고, pole 이 넘어져서 종료 state로 빠지면 0의 reward를 제공하도록 되어 있다. 본 예제에서는 pole이 넘어졌을 경우에 penalty를 크게 하기 위해 -10.0의 역 보상을 주도록 하였다. Training phase에는 epsion-greedy 정책에 따라 action을 선택하고, evaluation phase에서는 greedy 정책 기반으로 action을 선택하도록 하여 매 episode에서의 누적된 보상을 확인한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
import gymnasium as gym
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import copy
import torch
from dqn_agent import DQNAgent
def dqn():
env = gym.make('CartPole-v1')
learning_rate = 1e-3
gamma = 0.99
tau = 0.99
max_memory_size = 30000
batch_size = 64
N_EPISODE = 500
update_interval = 10
epsilon = 1.0
eps_decay_rate = 0.99
eps_min = 0.01
agent = DQNAgent(num_input_layers=4, num_output_layers=2, gamma=gamma, tau=tau, learning_rate=learning_rate, max_memory_size=max_memory_size)
agent_opt = copy.deepcopy(agent)
opt_model_para = copy.deepcopy(agent.dqn_net.state_dict())
opt_score = - np.Inf
opt_epi = 0
opt_score_eval = 0.0
opt_epi_eval = 0
SCORES = []
SCORES_eval = []
for n_epi in range(N_EPISODE):
epsilon = epsilon * eps_decay_rate
epsilon = max(eps_min, epsilon)
s, _ = env.reset()
s = np.expand_dims(s, axis=0)
done = False
score = 0.0
score_eval = 0.0
while not done:
action = agent.get_sample_action(s, epsilon)
s_prime, reward, done, truncated, _ = env.step(action)
s_prime = np.expand_dims(s_prime, axis=0)
score = score + float(reward)
done_mask = 0.0
if done or truncated:
if score > 499:
done_mask = 0.0
break
else:
reward = - 10.0
done_mask = 1.0
agent.memory.put((s, action, reward, s_prime, done_mask))
else:
agent.memory.put((s, action, reward, s_prime, done_mask))
s = s_prime
if agent.memory.size() > 500:
agent.train(batch_size)
SCORES.append(score)
s, _ = env.reset()
s = np.expand_dims(s, axis=0)
done = False
while not done:
action = agent.get_action(s)
s_prime, r_eval, done, truncated, _ = env.step(action)
score_eval = score_eval + float(r_eval)
if done or truncated:
break
s_prime = np.expand_dims(s_prime, axis=0)
s = s_prime
SCORES_eval.append(score_eval)
if score_eval >= opt_score_eval:
opt_score_eval = score_eval
agent_opt = copy.deepcopy(agent)
opt_model_para = copy.deepcopy(agent.dqn_net.state_dict())
opt_epi_eval = n_epi + 1
if score >= opt_score:
opt_score = score
opt_epi = n_epi + 1
print("N_epi: {}, Train score: {:.3f} \t Train eval score: {:.3f}, \t n_buffer: {}, \t epsilon: {:.3f}%"
.format(n_epi+1, score, score_eval, agent.memory.size(), epsilon * 100))
env.close()
print("Train opt score: {:.3f} @ episode: {}".format(opt_score, opt_epi))
print("Eval opt score: {:.3f} @ episode: {}".format(opt_score_eval, opt_epi_eval))
return agent, agent_opt, opt_model_para, SCORES, SCORES_eval
if __name__ == '__main__':
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
agent, agent_opt, opt_model_para, SCORES, SCORES_eval = dqn()
model = agent.dqn_net.to(device)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(10, 6))
ax[0].plot(SCORES)
ax[0].set_xlabel("Episode")
ax[0].set_ylabel("Training score")
ax[1].plot(SCORES_eval)
ax[1].set_xlabel("Episode")
ax[1].set_ylabel("Evaluation score")
fig.tight_layout()
4. 코드 실행 결과
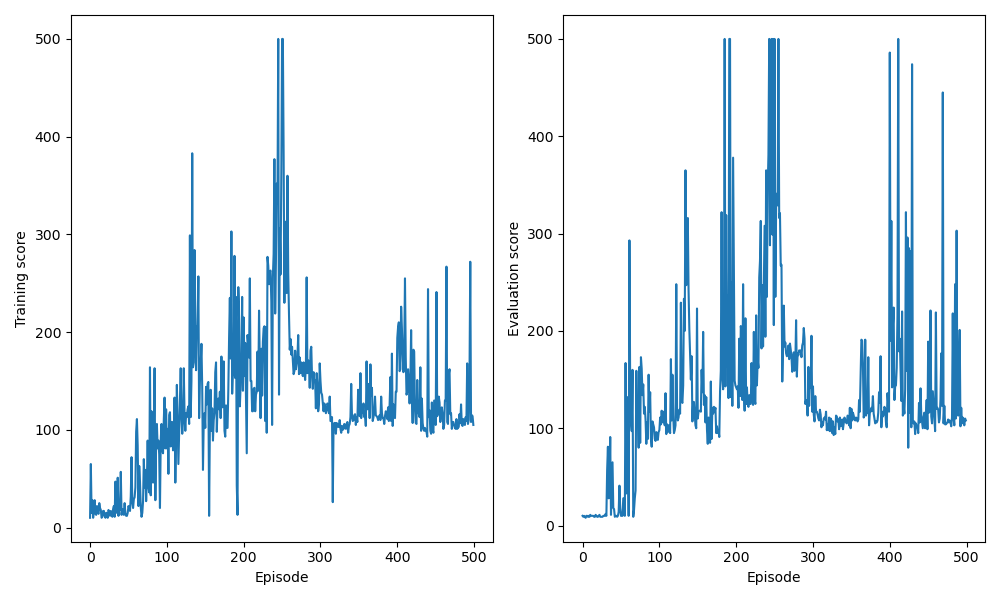
Main 함수를 실행시켜 학습 episode 동안 누적된 보상에 대한 결과를 출력하면 다음과 같다.
연산 환경에 따라 출력되는 결과는 상이할 수 있다.
학습이 episode가 지남에 따라 score 값이 증가되는 것이 확인되고, episode 초기에는 무작위로 action을 취할 때 score가 더 높지만 학습이 진행됨에 따라 DQN 모델의 weight가 업데이트 되며 greedy 정책 기반으로 action을 취할 때 score가 높아지는 것을 확인할 수 있다. Epsilon이 감소하면서 최대 step인 500회 까지 action이 진행되는 episode가 증가하는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
한편, episode에서 score를 보면 DQN 모델의 성능이 약간 불안정한 것이 확인되는데 추가로 개선된 DQN을 통해 학습 안정성을 높일 수 있다. 개선된 DQN과 관련된 내용은 이후 포스팅에서 다룬다.